In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one frontier that continues to captivate minds and reshape experiences is AR. At the core of this transformative technology lies the intricate workings of Face Recognition Software Development Kits (SDKs). In this detailed exploration, we embark on a journey to demystify the magic behind any Face SDK software, delving into their inner workings and understanding their profound impact on the world of AR.
Table of Contents
The Essence of Face Recognition in AR
Augmented Reality serves as the bridge between the physical and the digital world, enriching our surroundings with interactive and immersive experiences. Face Recognition technology, a crucial component of AR, takes this interaction to a deeply personal level. It involves the identification and verification of individuals through the unique features present in their facial structure.
How Face Recognition SDKs Operate
- Face Detection
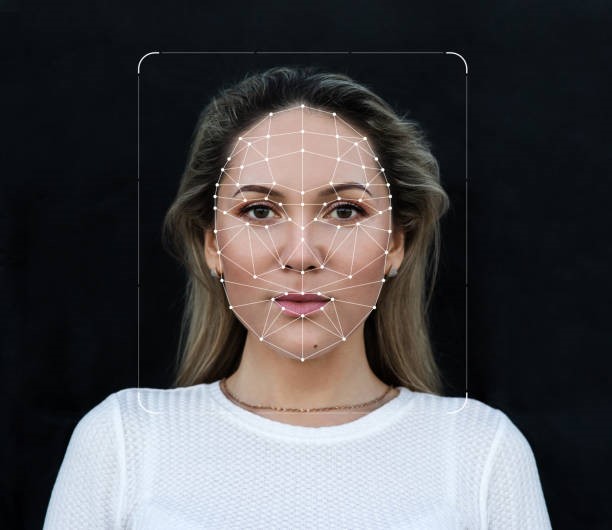
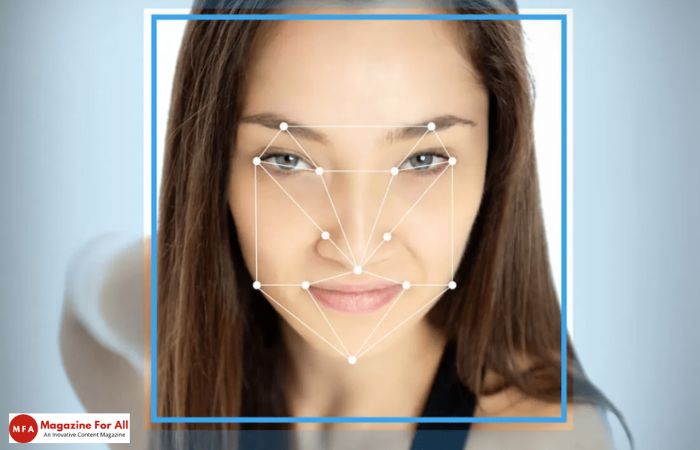
Face detection is the foundational process within Face Recognition SDKs, involving the implementation of sophisticated algorithms that meticulously analyze images or video streams. These algorithms possess the capability to identify and isolate key facial landmarks such as eyes, nose, and mouth. This initial step serves as the bedrock for subsequent analyses, laying the groundwork for the extraction of intricate facial features.
- Feature Extraction
Once a face is successfully detected, the Face Recognition SDK enters the phase of feature extraction. This intricate process involves the extraction of highly distinctive features from the identified face, culminating in the creation of a digital template or facial signature. This template is not a mere image but a comprehensive mathematical representation that encapsulates the unique characteristics and nuances of the individual’s facial structure. It becomes a digital fingerprint, serving as the basis for subsequent identification and verification processes.
- Database Matching
The extracted digital template undergoes a critical stage known as database matching. This involves a meticulous comparison between the acquired template and a database housing pre-existing templates of known individuals. The system scrutinizes the similarities and discrepancies, employing intricate algorithms to determine whether the identified face corresponds to an individual within its expansive database. This process is crucial for accurate identification and verification, forming the core mechanism of the Face Recognition SDK’s functionality.
- Continuous Learning
A hallmark of advanced Face Recognition SDKs is their integration of machine learning algorithms. This adaptive feature propels the system beyond static recognition capabilities, enabling it to evolve and enhance its accuracy over time. The machine learning algorithms embedded within the SDK facilitate a continuous learning process, allowing the system to adapt to variations in lighting conditions, diverse facial expressions, and other environmental factors. Through this continuous learning, the Face Recognition SDK becomes increasingly adept at fine-tuning its identification and verification processes, ensuring sustained accuracy and reliability. This dynamic aspect of continuous learning distinguishes advanced Face Recognition systems, making them resilient and capable of providing robust performance in a variety of real-world scenarios.
Applications and Implications
Security Enhancements:
- Implementing Face Recognition in security systems provides a robust layer of biometric authentication, surpassing the limitations of traditional passwords.
- Secure access to devices, confidential information, and physical spaces is augmented with facial recognition.
Personalized Digital Experiences:
- AR applications powered by Face Recognition SDKs can tailor experiences based on individual preferences.
- From personalized filters to interactive content, users can enjoy a customized and engaging digital environment.
Navigational Assistance:
- AR, with Face Recognition, offers intuitive navigational aids by overlaying contextual information on the user’s field of view.
- This personalizes the navigation experience, adapting it to individual preferences and requirements.
Conclusion
As we dive into the intricate workings of Face Recognition SDKs within the realm of Augmented Reality, the depth and breadth of their impact become increasingly apparent. Beyond the technological marvel, these SDKs usher in a new era of personalized, secure, and immersive digital experiences. Embracing this technology means embracing a future where the digital and physical seamlessly intertwine, creating a landscape where innovation knows no bounds.
Related post: How to download youtube shorts- youtube shorts download